In several stages of production, handling and application, air is incorporated so finely spread into resins, lacquers, and paints. Introduced air or gas can type spherical foam within the liquid section. In pure liquids, foam isn'tstable. Foam is merely stable in systems containing defoaming agent -like substances like wetting agents, or boundsurface management additives required to enhance vital properties of the paint. of these defoaming agent in paint have in common the very fact they'll migrate to the air/liquid interface of the paint, thereby reducing the physical phenomenon.

Defoaming agent apply to paint
CAUSES of froth
Foam could be a stable dispersion of a gas in an exceedingly liquid medium that results once a wetting agent layer forms around air foam and entrains them inside it. Air is incorporated into a coating by:
● mix throughout the polymer/pigment grinding and let-down steps.
● Pumping throughout package filling.
● Shear or spraying throughout application.
Foam is stabilised by totally different mechanisms via action of surfactants:
● Marangoni effects:The foam come back nearer along as a results of the attraction forces permitting the liquid to emanate of the froth and therefore the lamella to become dilutant and dilutant.
● static repulsion:The presence of ionic wetting agent molecules at the surface creates static repulsion.
● chemist snap:The foam lamella exhibits the next elasticity because of a stretching result caused by the presence of wetting agent molecules.
DEFOAMING MECHANISM
The principle of inhibiting or destroying foam (defoaming) is usually supported associate overcoming of the helpfulmechanisms. Foam management additives (defoaming agent in paint) possess properties that ar opposite to those required for foam stabilisation.
Foam management additives perform by a range of mechanisms to stop or rupture foam.
Their individual potency is set by three key factors:
● quality within the foaming medium. The quality of a defoaming agent in paint is vital for the movement of the defoaming agent in paint to the lamella.
● Low physical phenomenon, in order that they'll be uniformly spread throughout the formulation.
● Ability to penetrate into the froth wall (or lamella).
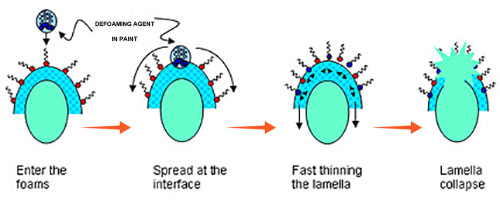
Defoaming Agent In Paint Eliminate Foam Mechanism
CHOOSING A FOAM management ADDITIVE
● Polysiloxanes:Modification of the polysiloxane backbone with gas leads to the alleged fluoro-silicones notedfor his or her terribly low physical phenomenon and powerful defoaming properties. For waterborne systems, a wider vary of chemical structures is used because of the commonly higher physical phenomenon of those systems.
● Mineral oil:As hostile solvent-based systems, the spreading of mineral oils in water-based systems is enoughto act as a foam management additive. within the presence of hydrophobic particles, the oil acts additionally as carrier for these particles, like hydrophobic silicon oxide or tinny soaps. attributable to the yellowing of the paint by the utilization of aromatic oil, open-chain oil is most popular.
● Silicone: Each dimethylpolysiloxanes and changed polysiloxanes is used as foam management agents in water-based systems.An important purpose to contemplate is that the incorporation of the froth management additive within the paint system. Since they're not soluble within the system, a decent distribution of the active substance is critical. this will be controlled by the blending speed and time, otherwise craters is shaped or loss of potency of defoaming agent in paint is ascertained.
 中文
中文
 EN
EN
